Cleveland Clinic survey finds most Americans don’t know their BMI, or that excess weight tips the scales for common heart conditions like coronary artery disease
images: 0
video: 2
audio: 0
text: 0
Content is property of Cleveland Clinic and for news media use only.


A Cleveland Clinic survey finds that while most Americans (88 percent) understand that there is a connection between a healthy heart and a healthy weight, most aren’t doing enough – or anything – to combat their own weight issues. The survey found 74 percent are concerned about their weight and 65 percent are worried about getting heart disease due to extra pounds, yet less than half (43 percent) of Americans have tried to make dietary changes to lose weight and 40 percent of those who describe themselves as overweight or obese say they aren’t careful about which foods they eat.
Part of the problem may be that Americans aren’t sure what to eat for heart health. Nearly one-in-five (18 percent) believe their diet has nothing to do with their heart health, and a mere 14 percent knew that a Mediterranean diet is healthiest for heart health. What’s more, nearly half of Americans (46 percent) believe using artificial sweeteners is a healthy way to lose weight despite studies showing they don’t promote weight loss.
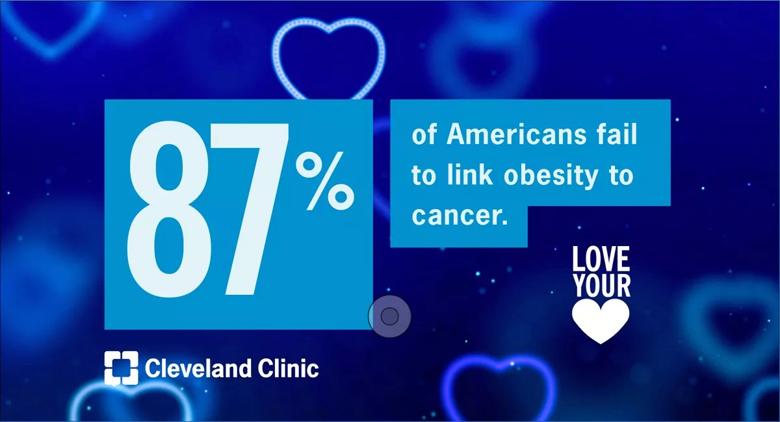
The survey also revealed Americans don’t fully understand the impact excess weight has on their heart and overall health. The overwhelming majority of Americans (87 percent) fail to link obesity to cancer or atrial fibrillation (80 percent). More than half of Americans also don’t know that obesity is linked to high “bad” cholesterol levels (54 percent) or coronary artery disease (57 percent) and two-thirds (64 percent) don’t know it can lead to a stroke.

“Most Americans understand abstractly that being overweight or obese is not good for your health, but it seems we are not grasping that the leading causes of death and disability – stroke, cancer, coronary artery disease – are all adversely affected by increased weight,” said Steven Nissen, M.D., chairman of Cardiovascular Medicine at Cleveland Clinic. “We need to do a better job of educating patients and the public about the major consequences of carrying excess weight and the benefits of losing weight. A patient only needs to lose five percent of their body weight to start seeing important health benefits.”
Eighty-four percent of Americans say they have tried at least one weight-loss method in the past. About one-third (30 percent) say they typically stick with it between one week and one month. Americans cite dislike of exercise (24 percent) and lack of time (22 percent) as their main barriers to maintaining a healthy weight. Most Americans also believe their metabolism is detrimental to weight loss – 60 percent of women and 46 percent of men say their metabolism is working against them.
A Cleveland Clinic survey finds Americans are concerned about their weight, but they don’t understand the link to heart conditions and overall health. #LoveYourHeart
Read more: https://t.co/XXAdUksP2m pic.twitter.com/PqmsBETVkr
— ClevelandClinicNews (@CleClinicNews) January 31, 2019
“Americans may be correct that their metabolism is thwarting their weight loss efforts,” said Dr. Nissen. “Once you’ve been overweight, your body tries to hold on to that excess fat, making it more difficult to lose weight. It’s best to work with your physician to develop a steady long term weight loss plan that will help you keep off the pounds. Quick weight loss programs are not effective.”
Heart disease is the No. 1 cause of death in the United States and around the world. The survey was conducted as part of Cleveland Clinic’s “Love your Heart” consumer education campaign in celebration of American Heart Month. Cleveland Clinic has been ranked the No. 1 hospital in the country for cardiology and cardiac surgery for 24 years in a row by US News & World Report.
Additional survey findings include:
According to the CDC, nearly 40 percent of Americans, 93 million people, are obese, and even more are overweight.
Methodology
Cleveland Clinic’s survey of the general population gathered insights into Americans’ perceptions of heart health and weight. This was an online survey conducted among a national probability sample consisting of 1,002 adults 18 years of age and older, living in the continental United States. The total sample data is nationally representative based on age, gender, ethnicity and educational attainment census data. The online survey was conducted by Research Now and completed between September 20 and September 28, 2018. The margin of error for the total sample at the 95% confidence level is +/- 3.1 percentage points.




About Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit multispecialty academic medical center that integrates clinical and hospital care with research and education. Located in Cleveland, Ohio, it was founded in 1921 by four renowned physicians with a vision of providing outstanding patient care based upon the principles of cooperation, compassion and innovation. Cleveland Clinic has pioneered many medical breakthroughs, including coronary artery bypass surgery and the first face transplant in the United States. U.S. News & World Report consistently names Cleveland Clinic as one of the nation’s best hospitals in its annual “America’s Best Hospitals” survey. Among Cleveland Clinic’s 52,000 employees are more than 3,600 full-time salaried physicians and researchers and 14,000 nurses, representing 140 medical specialties and subspecialties. Cleveland Clinic’s health system includes a 165-acre main campus near downtown Cleveland, 15 regional hospitals (11 in Ohio, four in Florida), more than 150 northern Ohio outpatient locations – including 18 full-service family health centers and three health and wellness centers – and locations in Las Vegas, Nev.; Toronto, Canada; Abu Dhabi, UAE; and London, England. In 2017, there were 7.6 million outpatient visits, 229,000 hospital admissions and 207,000 surgical cases throughout Cleveland Clinic’s health system. Patients came for treatment from every state and 185 countries. Visit us at clevelandclinic.org. Follow us at twitter.com/ClevelandClinic. News and resources available at newsroom.clevelandclinic.org.
Editor’s Note: Cleveland Clinic News Service is available to provide broadcast-quality interviews and B-roll upon request.