Novel system combines intuitive motor control with touch and hand movement sensation
images: 6
video: 1
audio: 0
text: 0
Content is property of Cleveland Clinic and for news media use only.
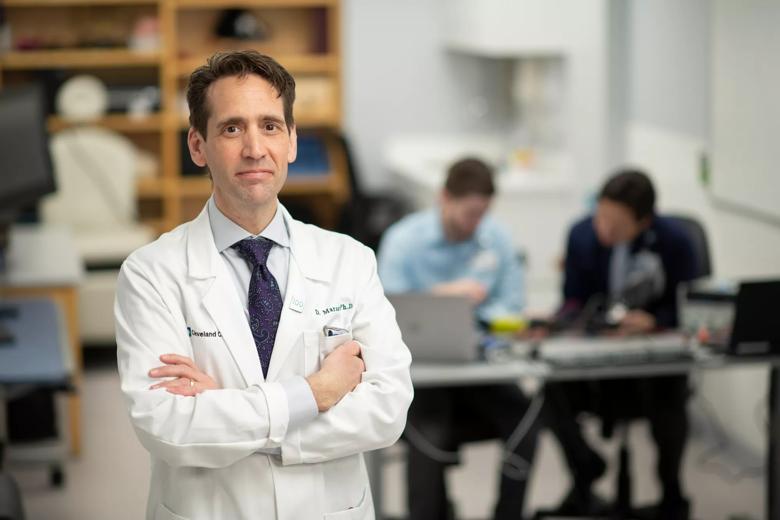


Cleveland Clinic researchers have engineered a first-of-its-kind bionic arm for patients with upper-limb amputations that allows wearers to think, behave and function like a person without an amputation, according to new findings published in Science Robotics.
The Cleveland Clinic-led international research team developed the bionic system that combines three important functions – intuitive motor control, touch and grip kinesthesia, the intuitive feeling of opening and closing the hand. Collaborators included University of Alberta and University of New Brunswick.
“We modified a standard-of-care prosthetic with this complex bionic system which enables wearers to move their prosthetic arm more intuitively and feel sensations of touch and movement at the same time,” said lead investigator Paul Marasco, Ph.D., associate professor in Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute’s Department of Biomedical Engineering. “These findings are an important step towards providing people with amputation with complete restoration of natural arm function.”
The system is the first to test all three sensory and motor functions in a neural-machine interface all at once in a prosthetic arm. The neural-machine interface connects with the wearer’s limb nerves. It enables patients to send nerve impulses from their brains to the prosthetic when they want to use or move it, and to receive physical information from the environment and relay it back to their brain through their nerves.

The artificial arm’s bi-directional feedback and control enabled study participants to perform tasks with a similar degree of accuracy as non-disabled people.
“Perhaps what we were most excited to learn was that they made judgments, decisions and calculated and corrected for their mistakes like a person without an amputation,” said Dr. Marasco, who leads the Laboratory for Bionic Integration. “With the new bionic limb, people behaved like they had a natural hand. Normally, these brain behaviors are very different between people with and without upper limb prosthetics.” Dr. Marasco also has an appointment in Cleveland Clinic’s Charles Shor Epilepsy Center and the Cleveland VA Medical Center’s Advanced Platform Technology Center.
The researchers tested their new bionic limb on two study participants with upper limb amputations who had previously undergone targeted sensory and motor reinnervation -procedures that establish a neural-machine interface by redirecting amputated nerves to remaining skin and muscles. Due to the study’s small size, additional research will be important.
In targeted sensory reinnervation, touching the skin with small robots activates sensory receptors that enable patients to perceive the sensation of touch. In targeted motor reinnervation, when patients think about moving their limbs, the reinnervated muscles communicate with a computerized prosthesis to move in the same way. Additionally, small, powerful robots vibrate kinesthetic sensory receptors in those same muscles which helps prosthesis wearers feel that their hand and arm are moving.
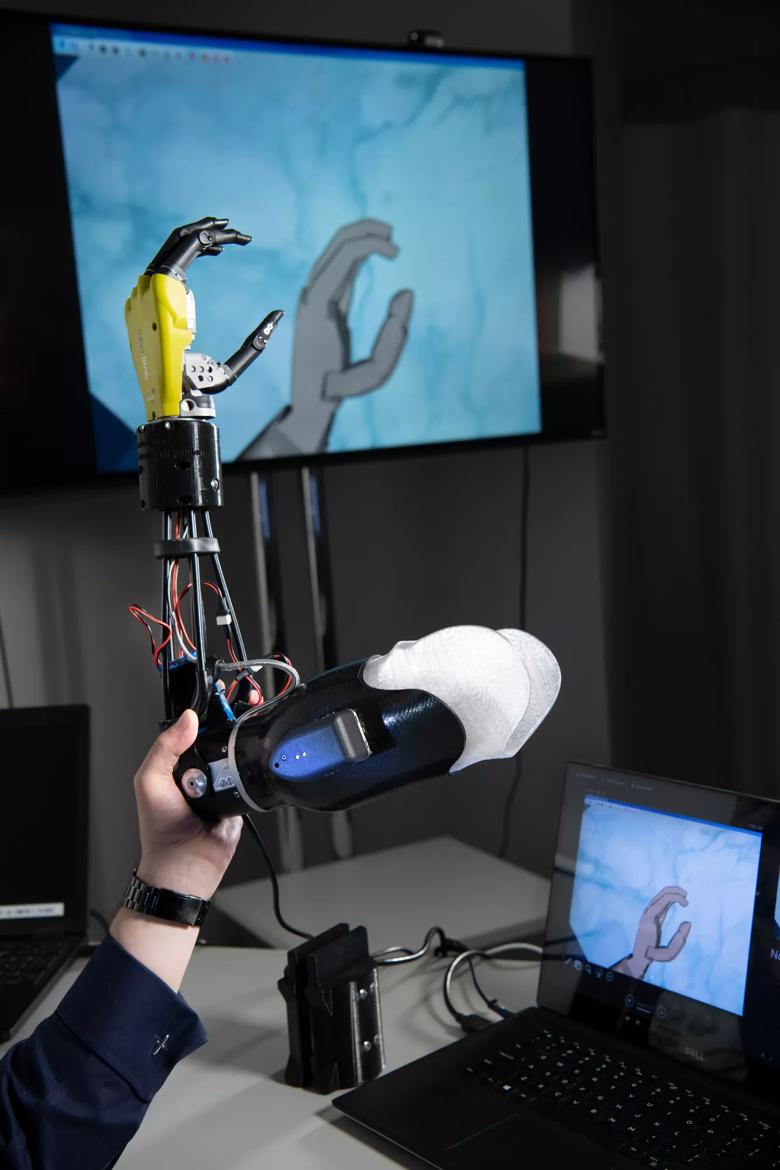

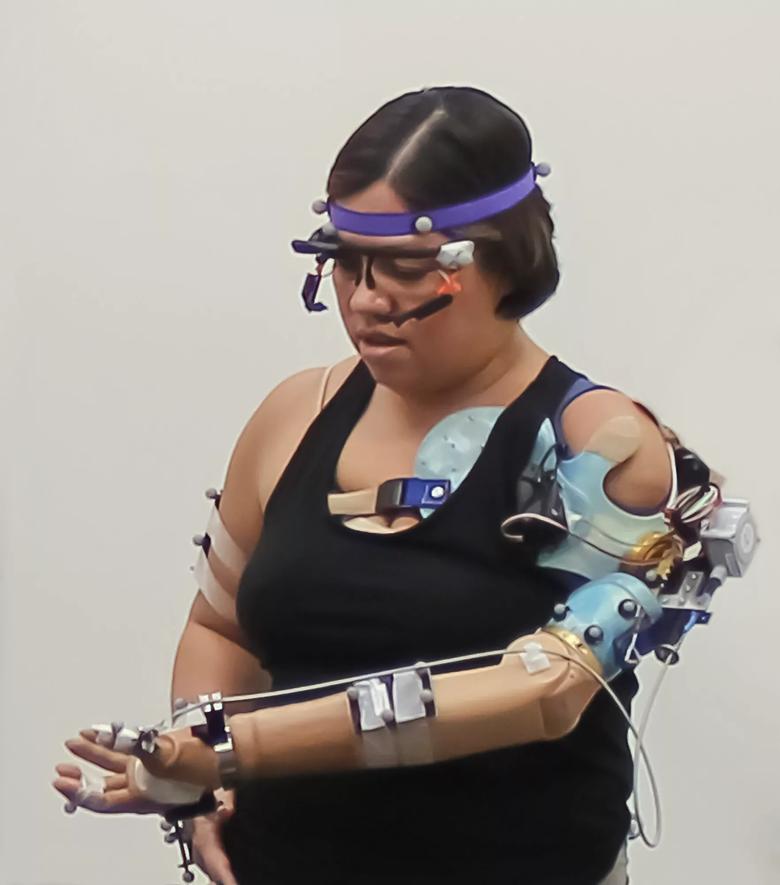
While wearing the advanced prosthetic, participants performed tasks reflective of basic, everyday behaviors that require hand and arm functionality. With their newly developed advanced evaluation tools, the researchers assessed how performance with the bionic limb compared to that of non-disabled people and people with amputations who have traditional prosthetic devices. They also compared how people with the advanced prosthetic fared when the three sensory and motor modalities were enabled together versus individually.
According to Dr. Marasco, because people with traditional prosthetics cannot feel with their limbs, they behave differently than people without an amputation while completing tasks during daily living. For example, traditional prosthesis wearers must constantly watch their prosthetic while using it and have trouble learning to correct for mistakes when they apply too much or little force with their hand.
With the new artificial arm and the advanced evaluation tools, the researchers could see that the study participants’ brain and behavioral strategies changed to match those of a person without an amputation. They no longer needed to watch their prosthesis, they could find things without looking, and they could more effectively correct for their mistakes.
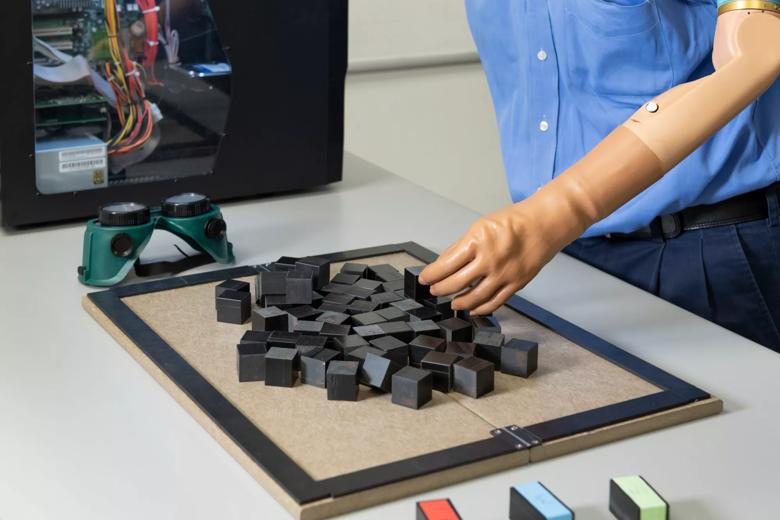

“Over the last decade or two, advancements in prosthetics have helped wearers to achieve better functionality and manage daily living on their own,” said Dr. Marasco. “For the first time, people with upper limb amputations are now able to again ‘think’ like an able-bodied person, which stands to offer prosthesis wearers new levels of seamless reintegration back into daily life.”
Beyond this study, the new outcome measurements related to brain behavior and functionality that the international team developed to evaluate the bionic system can be applied to any upper limb prosthetic or deficit that involves sensation and movement.
The study was funded in part by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, a research and development arm of the Department of Defense. In 2018, Dr. Marasco published a seminal paper in Science Translational Medicine on a new method of restoring natural movement sensation in patients with prosthetic arms.

Real and virtual prosthetic hand that are dexterous enough to represent all of the different hand movement sensations that each of the study participant can feel with their neural-machine interface.

The advanced prosthetic arm feels grip movement sensation, touch on the fingertips, and is controlled intuitively by thinking. Reflective markers on users’ arms and body help a computer see their movements in a 3D-environment, while glasses allow a computer to see exactly what they see.

The Prosthesis Efficiency and Profitability (PEP) test developed by Cleveland Clinic. This test provides insight into the types of decisions individuals make when trying to find different stiffness blocks among distractors using their senses of touch and grip kinesthesia.
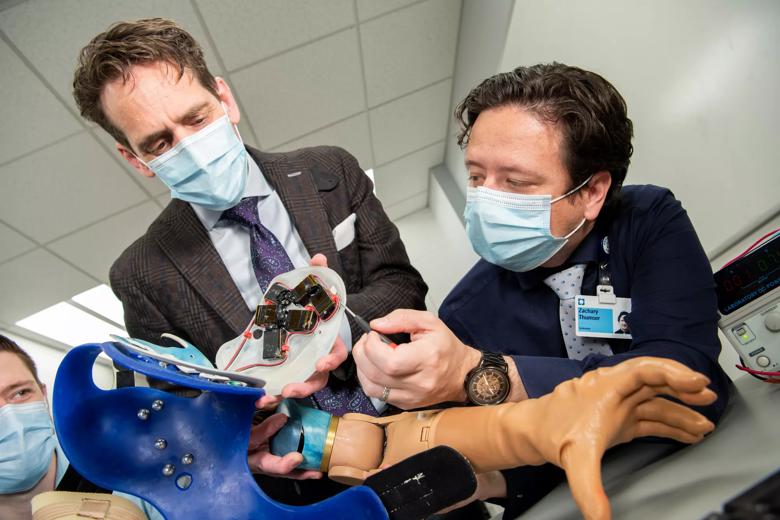

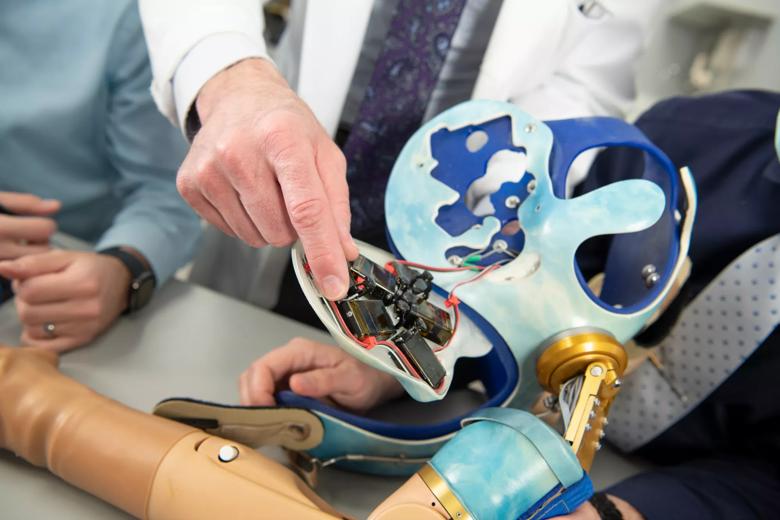
The research group in Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute’s Laboratory for Bionic Integration looking at the inside of the touch robot system. Each small black box provides individual finger sensation to the user through a neural-machine interface.

The robotic touch system inside of an advanced bionic limb. Each small black box provides individual finger sensation to the user through a neural-machine interface.
Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit multispecialty academic medical center that integrates clinical and hospital care with research and education. Located in Cleveland, Ohio, it was founded in 1921 by four renowned physicians with a vision of providing outstanding patient care based upon the principles of cooperation, compassion and innovation. Cleveland Clinic has pioneered many medical breakthroughs, including coronary artery bypass surgery and the first face transplant in the United States. Cleveland Clinic is consistently recognized in the U.S. and throughout the world for its expertise and care. Among Cleveland Clinic’s 82,600 employees worldwide are more than 5,786 salaried physicians and researchers, and 20,700 registered nurses and advanced practice providers, representing 140 medical specialties and subspecialties. Cleveland Clinic is a 6,728-bed health system that includes a 173-acre main campus near downtown Cleveland, 23 hospitals, 280 outpatient facilities, including locations in northeast Ohio; Florida; Las Vegas, Nevada; Toronto, Canada; Abu Dhabi, UAE; and London, England. In 2024, there were 15.7 million outpatient encounters, 333,000 hospital admissions and observations, and 320,000 surgeries and procedures throughout Cleveland Clinic’s health system. Patients came for treatment from every state and 112 countries. Visit us at clevelandclinic.org. Follow us at x.com/CleClinicNews. News and resources are available at newsroom.clevelandclinic.org.
Editor’s Note: Cleveland Clinic News Service is available to provide broadcast-quality interviews and B-roll upon request.